Metal casting is an ancient and versatile process that has been used to create metal objects for centuries. It involves the use of various methods and materials to shape molten metal into desired shapes.
This article provides an introduction to these methods and materials, discussing their history, benefits, limitations, applications, and more. By exploring different techniques such as die casting, sand casting, investment casting (lost wax), spin forming molding processes, and other unique forms of metalworking you will gain a better understanding of how this craft works.
Additionally, consider the advantages that modern technology brings in terms of accuracy and productivity while still respecting traditional practices. Finally, look at some examples of what can be achieved with metal casting so you can get creative ideas for your projects!
Overview of Metal Casting

Metal casting is the process of creating objects from molten metal. It has been used for centuries to create a variety of tools and materials, such as statues, jewelry, utensils, weapons, armor, and much more.
In modern times metal casting is used in many industries including automotive manufacturing and aerospace engineering. The process begins with designing or selecting a mold into which molten metal can be poured.
This mold must be able to withstand high temperatures without melting or warping during the casting procedure. Once the desired shape has been achieved in the mold it is cooled until it solidifies into its final form.
The material that results from this process may require additional processing before being ready for use; however, when done correctly metal castings provide an excellent result that can last for many years with minimal maintenance requirements.
Types of Metal Casting Processes

Metal casting is a form of manufacturing that involves pouring molten metal into a mold and allowing it to cool and solidify. It is one of the oldest forms of manufacturing, with evidence dating back thousands of years in many cultures around the world.
There are several different types of metal casting processes used today, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Die casting is a popular method for producing small parts from metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys.
It involves forcing molten metal under high pressure into steel molds called dies which can produce complex shapes quickly and accurately. The die castings have good surface finish characteristics but they tend to be expensive due to their intricate nature.
The investment or lost wax casting process utilizes reusable molds made from wax or other materials that are then filled with molten metal before being melted away when cooled down. This technique produces intricate details in low volumes but at a higher cost than some other methods due to the complexity involved in creating the molds themselves.
Sand Casting is another common method where sand-based mixtures are poured over patterns which create cavities once removed after cooling down; this process yields more economical parts than those produced by die or investment castings but its creations tend to require further finishing work afterwards since it often leaves rough surfaces on components created using this method.. Vacuum-assisted centrifugal casting offers an effective way of producing thin-walled shapes while eliminating traditional chaplets found in sand casting applications; this approach also generates less scrap material compared to typical sand casting processes making it an attractive option for certain projects requiring complex geometries without needing additional machining operations afterward. Finally, continuous centrifugal spinning creates round hollow components such as pipes or tubes directly from raw materials like liquid metals without having any need for intermediary steps providing great value when combined with fast production speeds achievable through this type of procedure thus making them ideal candidates for larger volume products needing quick turnaround times as well as increased precision levels throughout entire production cycles
Types of Materials Used in Metal Casting

Metal casting involves the use of a variety of materials, each with its unique properties and characteristics. Common metals used in metal casting include aluminum, brass, bronze, copper, iron, and steel.
Each has specific advantages when it comes to creating castings for applications such as automotive parts or architectural components. Aluminum is lightweight yet strong and durable; brass offers excellent corrosion resistance; bronze is well-suited to demanding industrial environments; copper is malleable and highly conductive; iron provides strength while remaining relatively inexpensive; and steel combines great strength with excellent wear resistance. In addition to these metals, other materials may also be employed during the metal casting process including sand molding material such as silica sand or olivine sand.
Sand molds are often preferred due to their low cost but they do come with certain drawbacks – they must be frequently replaced because of their high degree of thermal expansion which can lead to distortion in castings if not properly handled during cooling cycles. Waxes are another option for low-cost production runs especially when intricate shapes are required but waxes melt at relatively low temperatures making them less suited for some higher-temperature melts like those involving steels or alloys containing chromium or nickel elements.
Plastics may also be utilized but again there are tradeoffs – plastics have good heat resistance but tend to shrink more than other materials causing dimensional changes that need compensating allowances in design work to make up for the difference before final machining operations take place.
Safety Considerations for Working with Cast Metals
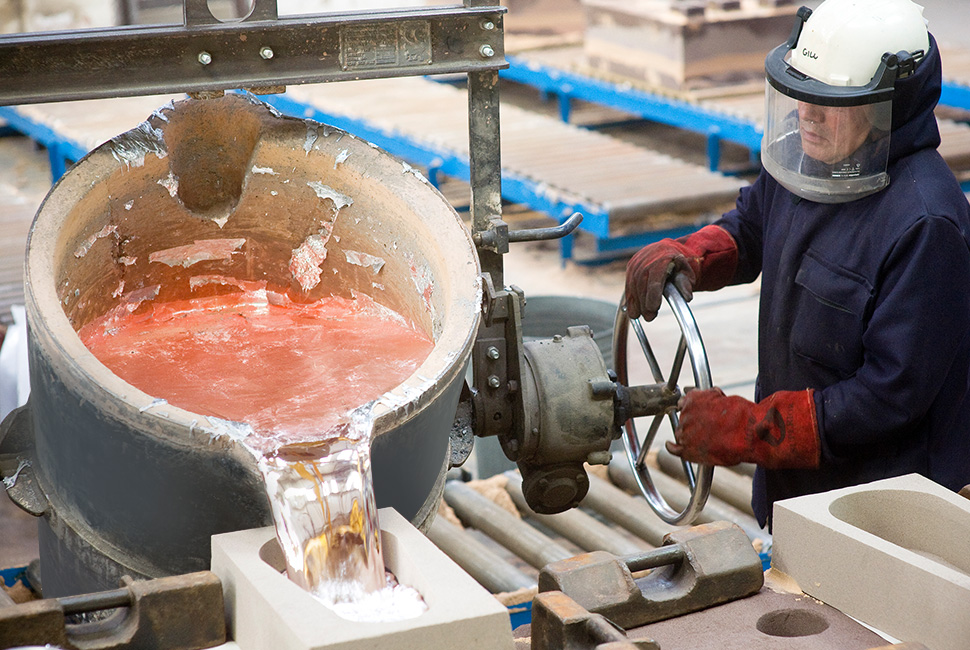

When it comes to metal casting, safety is a top priority. It is important to be aware of the potential hazards that come with working with molten metals and alloys as well as other materials used in the process.
To ensure safe practices for those handling cast metals, there are several considerations to take into account. To begin with, understanding the properties of different types of metals and their melting points is essential for properly carrying out any job involving metal casting.
For example, some metals are highly flammable or can cause burns if handled improperly. Also, personal protective equipment (PPE) should always be worn when dealing with these materials such as gloves, goggles, and face shields when necessary. In addition, having proper ventilation in any work area containing hazardous fumes from melted metal or dust created by grinding or machining processes also helps minimize exposure risks associated with them.
Good ventilation helps keep temperatures down which reduces fire risk and disperses toxic substances away from personnel working onsite safely and quickly. Finally, using a separate room dedicated solely to metal casting operations can help reduce cross-contamination between raw materials used in various production stages throughout any given project – this will help maintain quality control standards while minimizing health risks caused by contact with hazardous substances during manufacturing processes like molding or pouring molten alloy into molds.
Conclusion
Metal Casting is an effective and versatile method for producing customized parts of various sizes, shapes, and materials. It offers a wide range of possibilities in terms of design complexity, material strength, cost-effectiveness, and production speed.
With the right tools and techniques, a skilled metal casting specialist can create intricate components with precision and accuracy in short lead times. Utilizing this ancient process still proves to be worthwhile today as it provides manufacturers with reliable results at competitive costs.
Metal Casting remains one of the most trusted methods when it comes to producing complex custom parts that require tight tolerances from both hard metals and soft plastics.